Our Research
Evidence for leveraging change in nature-based solution policy and investment.
Research at the PiNC Lab explores the enablers and constraints of effective and equitable nature-based solutions across all phases including design, planning, implementation, maintenance, monitoring and evaluation. All projects at the lab fall within the below research themes. Read our full list of publications here.
Social impacts & equity
Our research examines the relationship between equitable and effective nature-based solutions, and how different solutions build adaptive capacity and reduce climate risks sensitivity.
Environmental impacts
We investigate ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies between nature-based solutions used for adaptation and mitigation, particularly for water-carbon couplings and food production.
Finance & capacity
We focus on understanding what factors and evidence types incentivise investment in equitable and effective nature-based solutions, and explore approaches that enable those in practice and policy to support this.
Governance
Our research examines the governance of nature-based solutions, aiming to shed light on how they can play a role in development that is just, sustainable and climate-resilient for all.
Featured publications
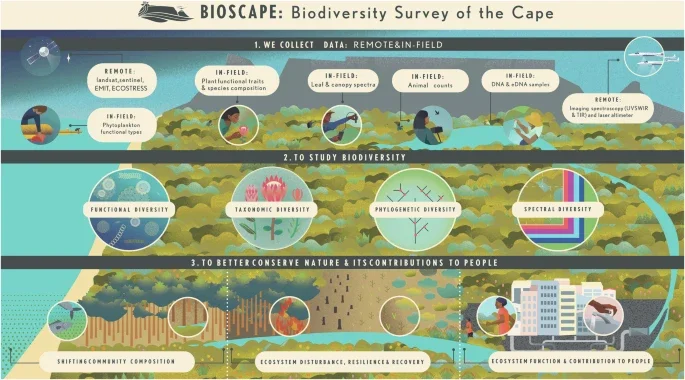
The Biodiversity survey of the Cape (BioSCape), integrating remote sensing with biodiversity science
Over six weeks, an international team of ~150 scientists collected data across terrestrial, marine, and freshwater ecosystems in South Africa. These biodiversity observations were accompanied by an unprecedented combination of airborne imaging spectroscopy and lidar measurements acquired across 45,000 km2. In this paper, published in Nature, researchers review how approaches applied in BioSCape will help measure and monitor biodiversity at scale and the role of remote sensing in accomplishing this.
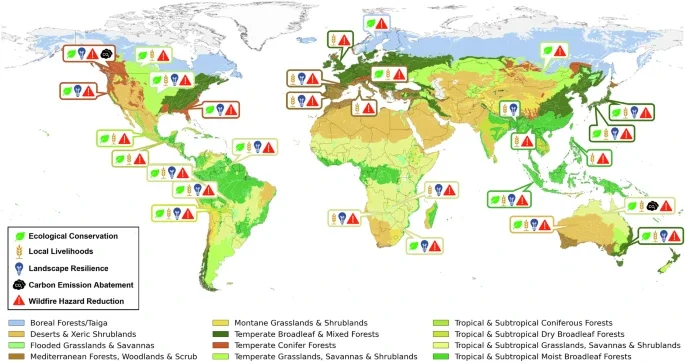
This review, published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, explores Integrated Fire Management as both an adaptation and mitigation strategy for altered fire regimes. It provides an overview of the progress and challenges associated with implementing Integrated Fire Management across different regions worldwide. The review also proposes five core objectives and outlines a roadmap of incremental steps for advancing Integrated Fire Management as a strategy to adapt to ongoing and future changes in fire regimes, thereby maximising its potential to benefit both people and nature.
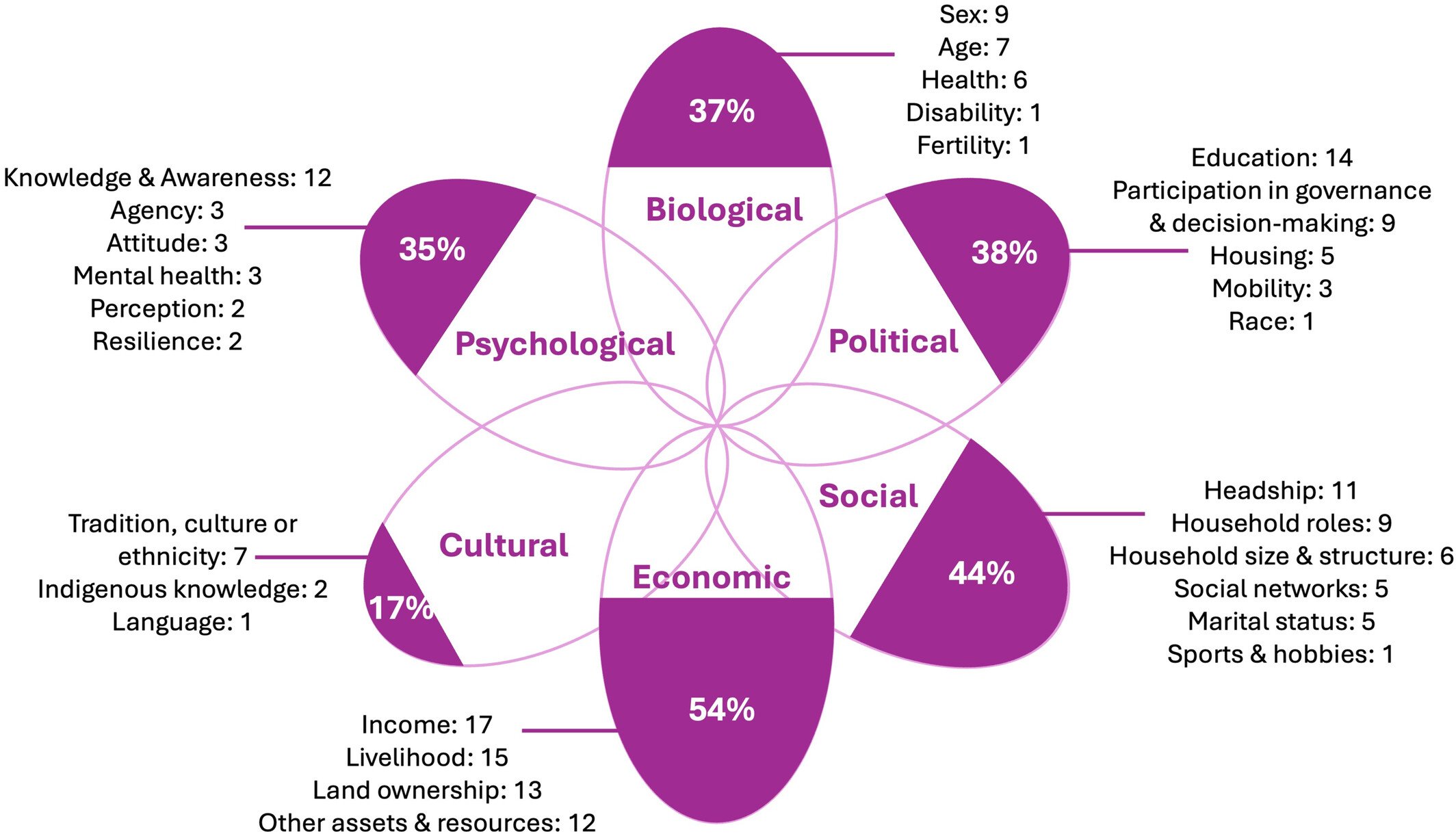
Understanding how gender inequality intersects with escalating climate change impacts is critical for informing climate adaptation responses that reduce vulnerability and inequality. To better understand gendered vulnerability, this study published in the journal WIREs Climate Change, develops and applies an intersectional climate risk framework, based on a systematic literature review of 52 articles. South Africa is used as a case study to apply the framework to understand how climate hazards (such as changing temperatures, droughts, and floods) exacerbate conditions of poverty and poor infrastructure and services, and the impact on women.